For reference: The Paris Agreement | Part 1
In our previous article, we explored the essence, goals, and challenges of The Paris Agreement. As we continue our deep dive, Part 2 focuses on the specific mechanisms, successes, and ongoing efforts to uphold the commitments made under this landmark accord. Understanding these elements is crucial for appreciating the comprehensive nature of The Paris Agreement and its role in shaping a sustainable future.
Mechanisms of The Paris Agreement
Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs)
Each country submits its NDCs outlining plans to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate impacts. These contributions reflect each nation’s capabilities and circumstances, allowing for flexibility while aiming for ambitious climate action.
Global Stocktake
Every five years, starting in 2023, a global stocktake assesses collective progress toward achieving the Agreement’s long-term goals. This process helps to identify gaps, share best practices, and encourage nations to enhance their climate commitments.
Climate Finance
Developed countries are urged to provide financial resources to assist developing nations in their climate actions. This includes funding for mitigation, adaptation, and technology transfer, fostering a collaborative effort to address global climate challenges.
Transparency Framework
The Agreement includes a robust transparency framework to track and report on nations’ progress. This ensures accountability and builds trust among countries, as they are required to submit regular reports on their emissions and implementation efforts.
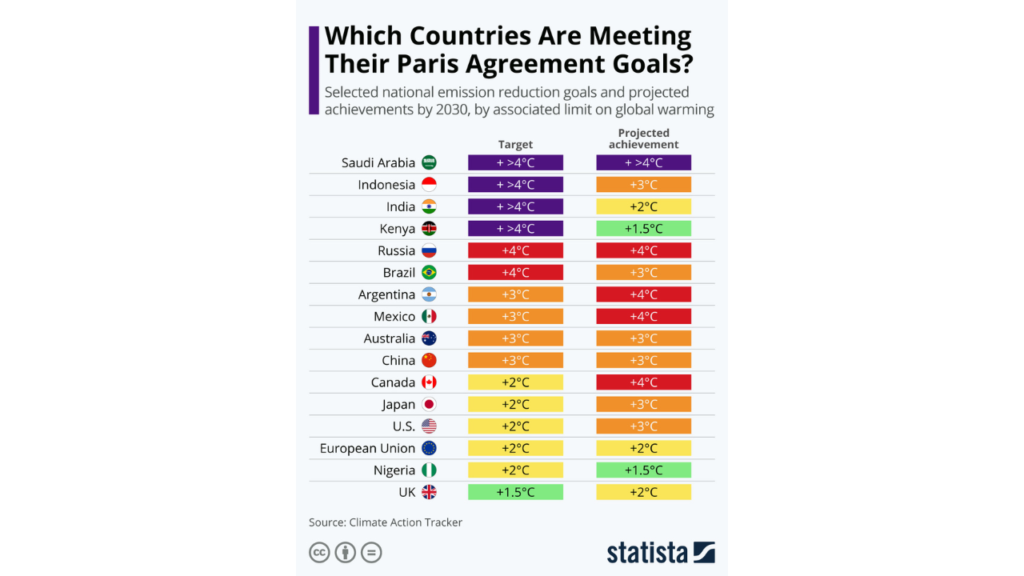
Successes of The Paris Agreement
Increased Ambition
Since the adoption of The Paris Agreement, many countries have raised their climate ambitions, setting more aggressive targets for reducing emissions. This collective effort signifies a growing recognition of the urgent need to address climate change.
Renewable Energy Growth
The Agreement has catalyzed a significant increase in renewable energy investments. Solar, wind, and other renewable sources have seen rapid expansion, contributing to a reduction in global carbon emissions.
Private Sector Engagement
The Paris Agreement has spurred private sector involvement in climate action. Many companies have set net-zero targets and are investing in sustainable practices, recognizing the economic and reputational benefits of aligning with global climate goals.
Ongoing Efforts and Future Directions
Enhancing NDCs
Nations are encouraged to continuously update and strengthen their NDCs. By implementing robust policies and measures to achieve these commitments, the global temperature goals can remain within reach.
Addressing Climate Adaptation
While mitigation efforts are crucial, adaptation to climate impacts is equally important. The Paris Agreement emphasizes the need for resilience-building in vulnerable communities, enhancing their capacity to cope with climate-related challenges.
International Collaboration
Continued international cooperation is essential for achieving the Agreement’s goals. Collaborative research, technology sharing, and capacity-building initiatives can help bridge gaps and support countries in their climate efforts.
Mobilizing Climate Finance
Securing adequate financial resources remains a priority. Developed nations must fulfill their funding commitments, and innovative financing mechanisms should be explored to support climate actions in developing countries.
The Paris Agreement represents a monumental step in the global fight against climate change. Its comprehensive framework, grounded in cooperation and flexibility, provides a dynamic platform for real progress. However, achieving its ambitious goals requires unwavering commitment, innovation, and collaboration from all nations. As we move forward, the continued enhancement of climate actions and support for vulnerable communities will be crucial in ensuring a sustainable and healthy planet for future generations.
Author
Ziara Walter Akari
© www.apotheosislife.com
