As the impacts of climate change become increasingly apparent, the need for resilience and adaptation is more urgent than ever. Climate resilience refers to the ability of communities, ecosystems, and economies to withstand and recover from the effects of climate change. Adaptation involves making adjustments to practices, systems, and infrastructure to reduce vulnerability to climate-related risks. This article explores the importance of climate resilience and adaptation, along with strategies to build a more sustainable and resilient future.
Understanding Climate Resilience and Adaptation
Climate Resilience: Climate resilience is the capacity to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and recover from climate-related hazards. It involves strengthening systems and structures to minimize damage and ensure that communities and ecosystems can bounce back quickly from adverse events.
Climate Adaptation: Adaptation refers to the process of making practical changes to reduce the negative impacts of climate change. This includes modifying infrastructure, altering agricultural practices, and developing policies that support climate-smart planning and decision-making.
Why Climate Resilience and Adaptation Matter
Protecting Communities: Climate change poses significant risks to communities around the world, including more frequent and intense storms, heatwaves, droughts, and sea-level rise. Building resilience helps protect lives, property, and livelihoods from these threats.
Sustaining Economies: Economies are increasingly vulnerable to climate-related disruptions, from agricultural losses to damaged infrastructure. Adaptation measures can help sustain economic growth by ensuring that businesses and industries can continue to operate under changing climate conditions.
Preserving Ecosystems: Healthy ecosystems are essential for human survival, providing services such as clean water, food, and air. Climate adaptation strategies can help preserve these ecosystems, ensuring that they continue to function despite environmental changes.
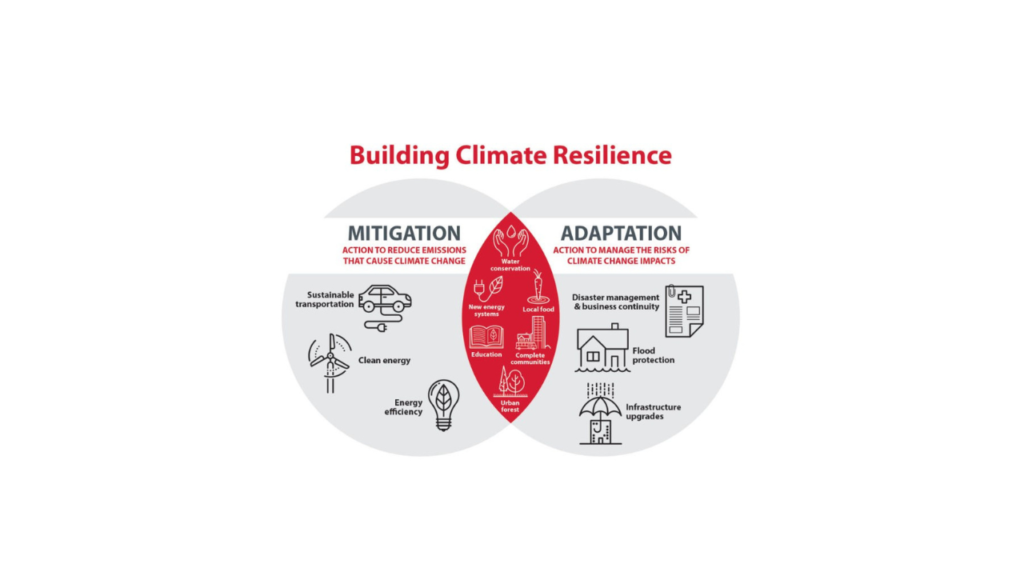
Image: Pangea Giving
Strategies for Building Climate Resilience and Adaptation
Infrastructure Development: Building climate-resilient infrastructure is crucial for reducing vulnerability to extreme weather events. This includes constructing flood defenses, retrofitting buildings to withstand storms, and designing transportation systems that can function under adverse conditions.
Sustainable Agriculture: Climate-smart agriculture involves using farming practices that increase productivity while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing resilience to climate impacts. This includes crop diversification, water management, and soil conservation techniques.
Community-Based Adaptation: Empowering communities to take action on climate adaptation is essential for building resilience at the local level. This involves engaging communities in decision-making processes, providing education and resources, and supporting local adaptation initiatives.
Policy and Governance: Effective climate adaptation requires strong policies and governance frameworks. Governments play a key role in setting regulations, providing funding for adaptation projects, and fostering collaboration between public and private sectors.
Ecosystem Restoration: Restoring degraded ecosystems, such as wetlands, forests, and coastal areas, can enhance their natural resilience to climate impacts. Ecosystem-based adaptation leverages the natural ability of ecosystems to buffer against climate-related hazards.
The Role of Innovation and Technology
Early Warning Systems: Advanced technology can provide early warnings for extreme weather events, giving communities time to prepare and respond. These systems can significantly reduce the impact of climate-related disasters.
Renewable Energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also enhances energy security and resilience. Renewable energy systems are less vulnerable to climate-related disruptions compared to traditional fossil fuel-based systems.
Data and Analytics: Big data and analytics play a critical role in climate adaptation by providing insights into climate trends, risks, and vulnerabilities. This information is vital for making informed decisions and planning effective adaptation strategies.
Climate resilience and adaptation are essential components of the global response to climate change. By investing in resilient infrastructure, adopting sustainable practices, and fostering innovation, we can build a future where communities, economies, and ecosystems can thrive despite the challenges posed by a changing climate. As the impacts of climate change continue to unfold, the urgency to act has never been greater. It is up to all of us to ensure that we are prepared for what lies ahead.
Author
Ziara Walter Akari
© www.apotheosislife.com
